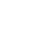

Return the absolute value of the input parameter x.
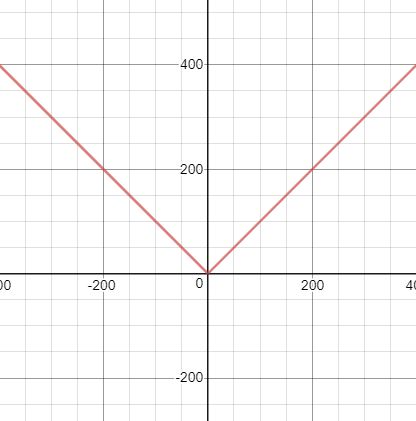
Input parameter x value range is [-1,1], returns the angle value range is [0, π]
Returns true if input parameter x is not 0; otherwise returns false.
Returns true if a boolean scalar or any component of a boolean vector is true; otherwise return false.
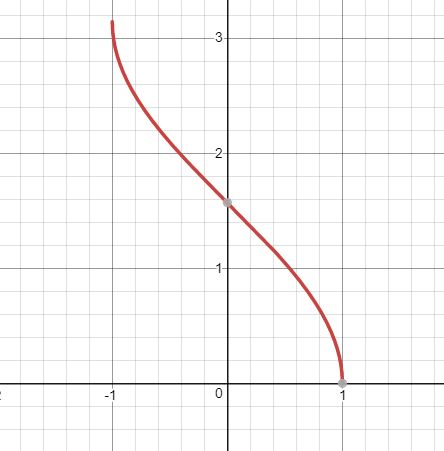
Input parameter x value range is [-1, 1], return angle value range is [–π/2, π/2]

The inverse tangent function, the return angle value range is [–π/2, π/2]
Calculate the arctangent of y/x. In fact, it has almost exactly the same function as the atan(x) function, and the input parameters are different (used to prevent the error case where the division denominator is 0). Atan(x) = atan2(x, float(1)).

Round up the input parameter x. For example: ceil(float(1.3)) with a return value of 2.0

Returns x clamped to the range [a,b]
- Returns a if x is less than a; else
- Returns b if x is greater than b; else
- Returns x otherwise.
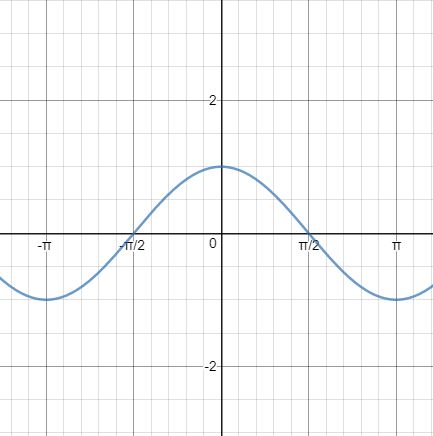
Returns the cosine of a in radians. The return value range is [-1,1]
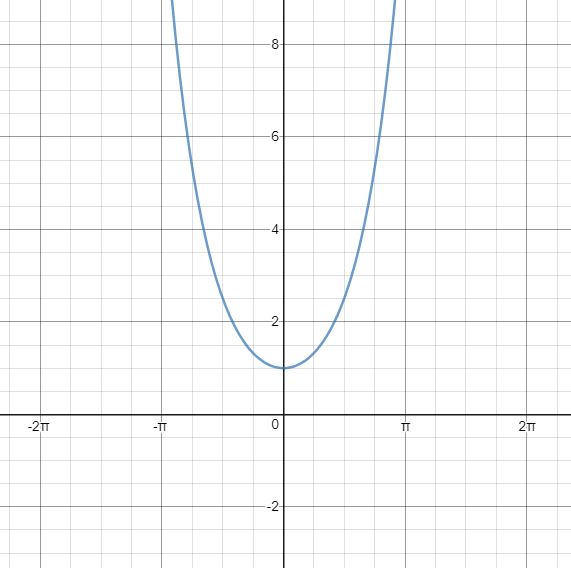
The hyperbolic cosine function calculates the hyperbolic cosine of x
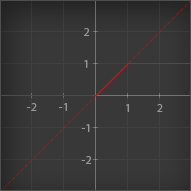
Returns the cross product of two vectors.
Notethat the input parameter must be a ternary vector!
Input parameter x is radians, return degree.
return the determinant factor of the matrix.
Return the dot product of a and b
Return the result of $e^x$ (e = 2.71828182845904523536)
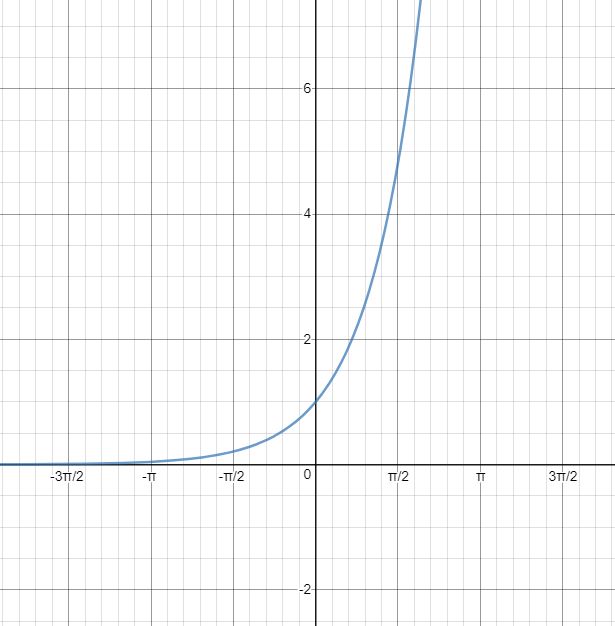
Return the result of $2^x$

Round down the input parameters.For example, floor(float(1.3)) returns a value of 1.0
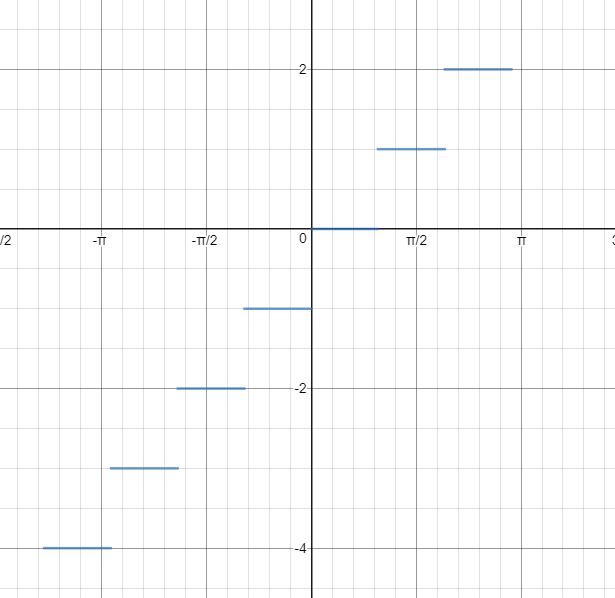
returns the remainder of x/y with the same sign as x
Returns the decimal of a value or vector
Splits scalars and vectors into normalized fraction and a power of 2
x: Vector or scalar of which to split.e: Vector or scalar where the exponent of x is output.
return the inverse matrix of a matrix
Returns whether or not a scalar or each vector component is a finite value.
Returns whether or not a scalar or each vector component is a (negative or positive) infinite value.
Returns whether or not a scalar or each vector component is not-a-number (NaN) Finite and infinite values are not NaN.
returns x times 2 raised to the power n. $x * 2^n$
Interpolate between lower limit a and upper limit b, and f represents the weight. $(1 – f )* a + b * f$
Note: that if a and b are vectors, the weight f must be a scalar or a vector of equal length.
The lit function is a helper function useful to compute lighting coefficients for ambient, diffuse, and specular lighting contributions. The function efficiently maps to a native instruction for most GPUs.
- Input parameters:
NdotL: The dot product of a normalized surface normal and a normalized light vector.NdotH: The dot product of a normalized surface normal and a normalized half-angle vector.m: A specular exponent, typically described as a measure of shininess. The larger the exponent, the shinier the specular highlight, the smaller the exponent, the duller the specular highlight.- Returns a 4D vector:
x: The ambient coefficient that is always 1.0.y: The diffuse coefficient that is zero if NdotL is less than zero, and NdotL otherwise.z: The specular coefficient that is zero if either NdotL or NdotH are less than zero, and otherwise NdotH raised to the power m.w: Always 1.0.
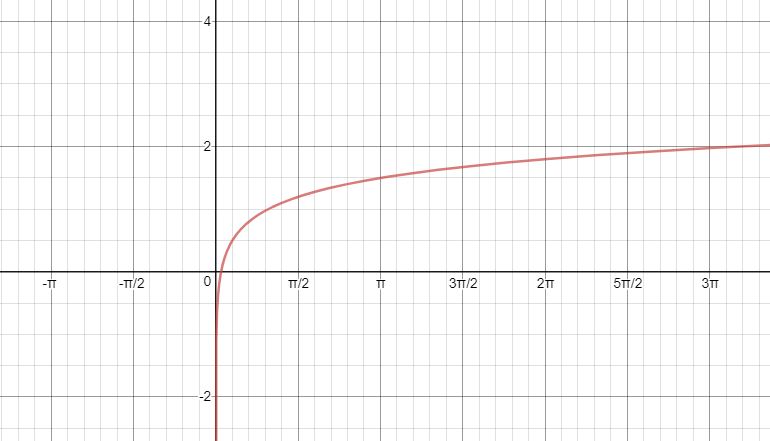
Returns the natural logarithm a (ln(x)).

Returns the base-2 logarithm a.

Returns the base-10 logarithm a.
returns the maximum of two scalars or each respective component of two vectors.
returns the minimum of two scalars or each respective component of two vectors.
Decompose x into two parts, an integer and a fraction. Each part has the same sign as x, the integer part is stored in ip, and the fractional part is returned by the function.
Returns the product of matrix M and matrix N.

Returns the product of Matrix M and Vertical Vector v.
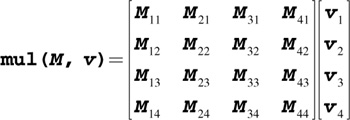
Returns the product of Horizontal Vector v and Matrix M.

return the result of $x^y$
Degree to Radian
Returns a rounded value
The inverse of the square root of x(x has to be greater than 0)
Limit x to [0,1]
Returns positive one, zero, or negative one for each of the components of x based on the component’s sign.
- Returns -1 component if the respective component of x is negative.
- Returns 0 component if the respective component of x is zero.
- Returns 1 component if the respective component of x is positive.
- Ideally, NaN returns NaN.
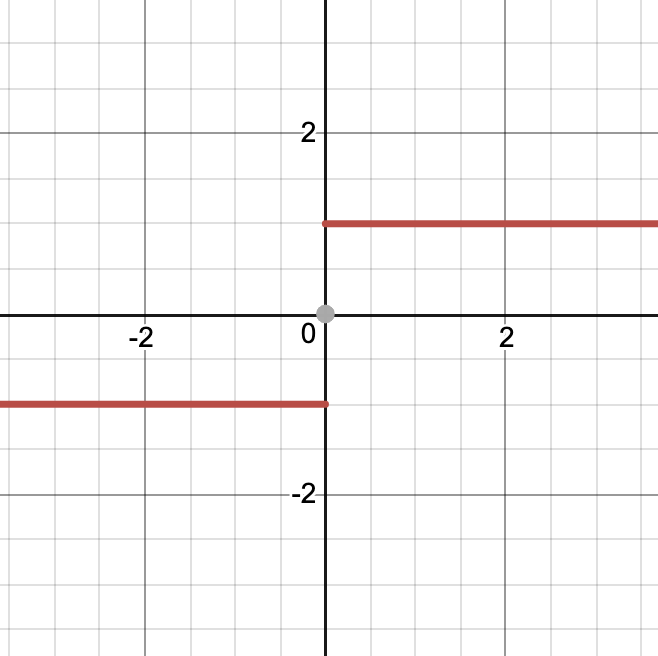
Limit x to [0,1]
Returns the sine of a in radians. The return value is in the range [-1, 1].
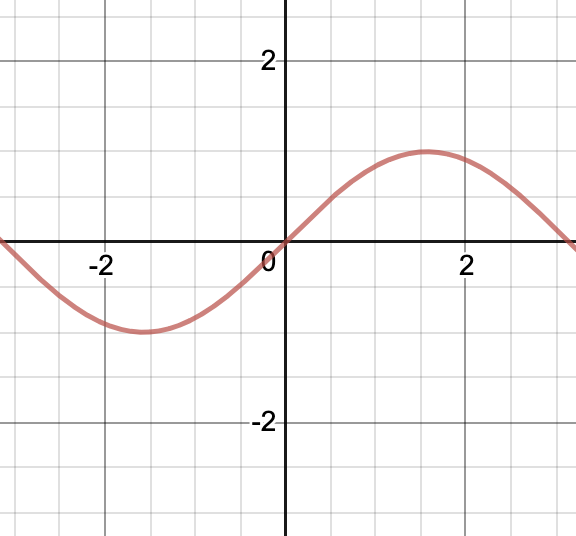
Calculate the sine and cosine at the same time, where s = sin(x) and c = cos(x). (faster than doing them separately)
Returns the hyperbolic sine of x
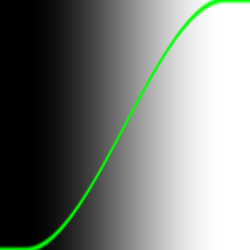
Interpolates smoothly from 0 to 1 based on x compared to a and b.
- Returns 0 if x < a < b or x > a > b
- Returns 1 if x < b < a or x > b > a
- Returns a value in the range [0,1] for the domain [a,b].
Implement a step function returning either zero or one for each component of x
if x<a:
return 0
else:
return 1

Find the square root of x, $\sqrt{x}$ (x must be greater than 0)
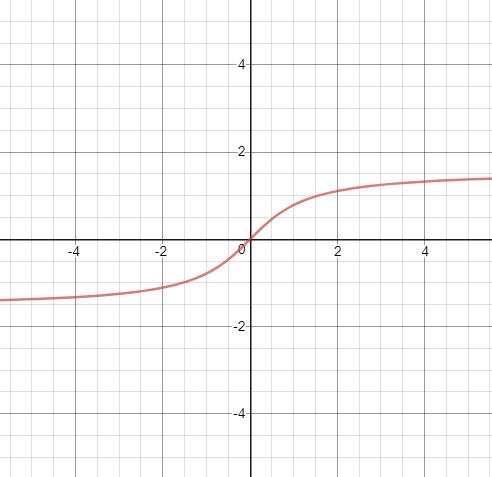
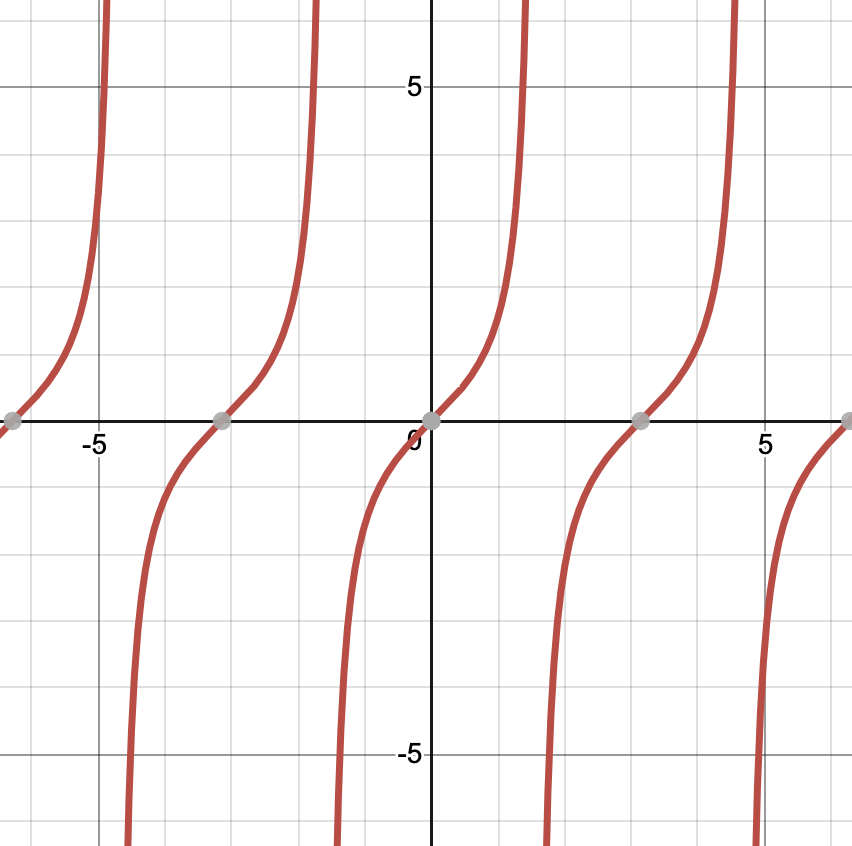
Returns the tangent of x in radians.
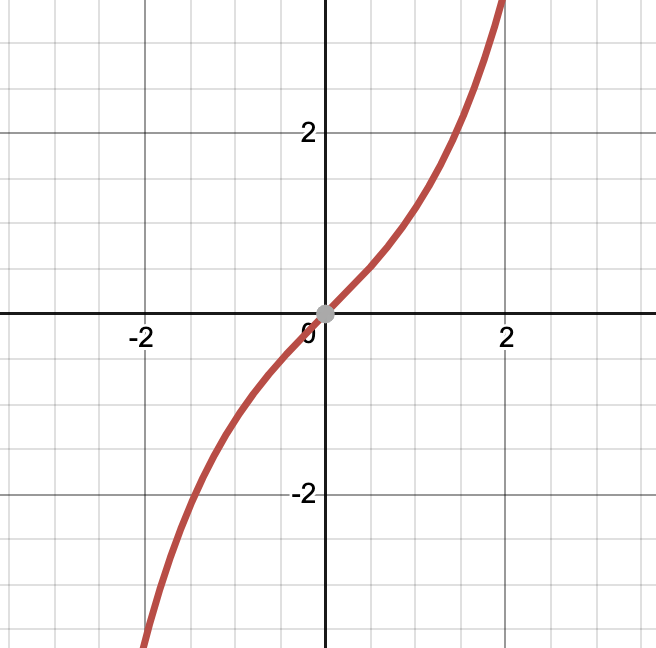
Returns the hyperbolic tangent of x.

Returns the transpose of the matrix M.
returns the distance between a and b
Returns a normal as-is if a vertex’s eye-space position vector points in the opposite direction of a geometric normal, otherwise return the negated version of the normal.
if dot(Ng,I)<0 return N else return -N
returns the magnitude of a vector;
sqrt(dot(v,v))
returns a normalized vector $ V_n = \frac{\overrightarrow{V}}{|\overrightarrow{V}|}$
returns the magnitude of a vector;
sqrt(dot(v,v))
The reflection vector is calculated according to the incident ray direction I and the surface normal vector N
function reflect(I, N) { return I - 2.f * Dot(I, N) * N; }
The refraction vector is calculated from the incident ray direction I, the surface normal vector N and the refraction relative coefficient eta. If the angle between I and N is too large for a given eta, return (0,0,0). (Only valid for ternary vectors)
function refract(I, N, eta) { float N_dot_I = dot(N, I); float k = 1.f - eta * eta * (1.f - N_dot_I * N_dot_I); if (k < 0.f) out = float3(0.f, 0.f, 0.f); else out = eta * I - (eta * N_dot_I + sqrt(k)) * N; }
Performs a texture lookup in sampler samp using coordinates s, may use and derivatives dx and dy, also may perform shadow comparison and use texel offset texelOff to compute final texel.
Performs a texture lookup with specified level of detail and optional texel offset.
Performs a texture lookup with projection in a given sampler. May perform a shadow comparison if argument for shadow comparison is provided.
Performs a texture lookup in a given sampler array may use pre computed derivatives and, in some cases, perform a shadow comparison.
Performs a texture array lookup with specified level of detail and optional texel offset.
Performs a texture lookup with projection in a given sampler array. May perform a shadow comparison if argument for shadow comparison is provided.
Returns approximate partial derivative with respect to window-space X
Returns approximate partial derivative with respect to window-space Y
Returns sum of approximate window-space partial derivatives magnitudes
If DEBUG is set at compile time, calling this function in the fragment coloring program can use the value x as the final output of the COLOR semantics; otherwise the function does nothing.
End –Cheng Gu