
One of the most commonly used command in maya.cmds API is cmds.ls(), this command will return a list that contains all objects in the scene.
We can list the selected object by set the selection flag to True, as belows:
cmds.ls(selection=True)
When we want to check the type of the object. For example, we want to know if the object is a mesh type, we can do by using cmds.listRelatives() and cmds.nodeType() as following:
# get the shape of the object
shapeNode = cmds.listRelatives(obj, shapes=True)
# get the node type through shape
nodeType = cmds.nodeType(shapeNode)
# if the type is "mesh", return true
if nodeType == "mesh":
return True
If we want to get the counts on the specified object cmds.polyEvaluate(). For example, do as following to get the number of vertices, edges, and faces:
vertNum = cmds.polyEvaluate(obj,vertex=True)
edgeNum = cmds.polyEvaluate(obj,edge=True)
faceNum = cmds.polyEvaluate(obj,face=True)
Sometimes we want to get the reference from the specific vertex, edge, or face. The following code shows to select the specific vertex, edge, and face by using cmds.select
cmds.select(obj+".vtx[0]",replace=True)
cmds.select(obj+".e[1:5]",replace=True)
cmds.select(obj+".f[-1]",replace= True)
Using cmds.getAttr() to retrieve the value of specified attribute on a given node.
degU = cmds.getAttr(obj+".degreeU")
spansU = cmds.getAttr(obj+".spansU")
cvsU = degU+spansU
print("CVs (U): %s"%cvsU)
degV = cmds.getAttr(obj+".degreeV")
spansV = cmds.getAttr(obj+".spansV")
cvsV = degV+spansV
print("CVs (V): %s"%cvsV)
Using cmds.curve() to create curve.
cmds.curve(degree=1,p=[(-0.5,-0.5,0),(0.5,-0.5,0),(0.5,0.5,0),(-0.5,0.5,0),(-0.5,-0.5,0)])
Using cmds.polyCreateFacet() to create polygon faces.
# Create a triangular facet
cmds.polyCreateFacet( p=[(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), (10.0, 0.0, 0.0), (10.0, 10.0, 0.0)] )
# Create a quadrangular facet with two triangular holes inside
# Note that, in Python, specifying an empty tuple in the point list marks the
# beginning of a hole specification
cmds.polyCreateFacet( p=[(0, 0, 0), (10, 0, 0), (10, 10, 0), (0, 10, 0), (), (4, 2, 0), (5, 4, 0), (6, 2, 0), (), (5, 6, 0), (4, 8, 0), (6, 8, 0)] )
cmds.move( 0, 0, 10, r=True )
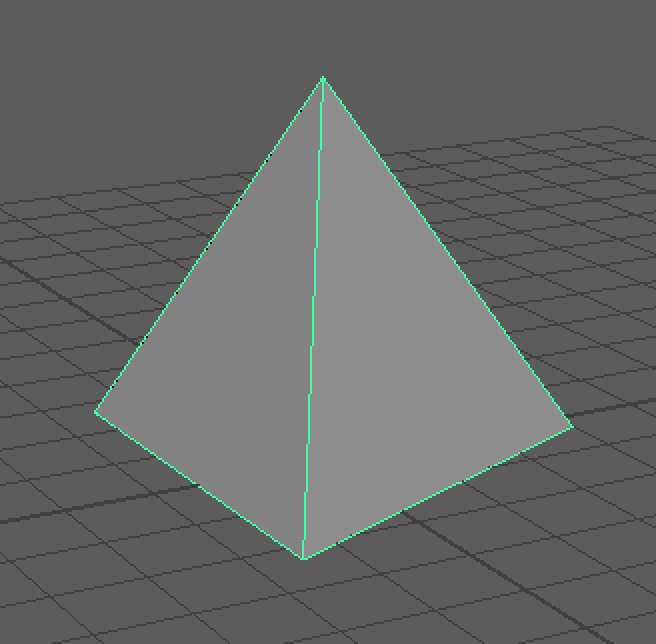
An example of create a tetrahedron by using cmds.append() to append faces, cmds.polyUnite() to combine faces, [cmd.polyMergeVertex()] to merge vertices, cmds.move() to move the points, [cmds.xform()] to transform the pivot of the object, finally using cmds.makeIdentity() to freeze transformation, and using cmds.delete() to delete construction history.
from maya import cmds
import math
def makeTetra(size):
pointA = [0,0,0]
pointB = [size,0,0]
pointC = [size/2,0,0]
# set the z position for C
pointC[2] = math.sqrt((size*size)-(size/2*size/2))
pointE = [0,0,0]
#average the A, B, and C to get E
# add all the values
for i in range(0,3):
pointE[i]+=pointA[i]
pointE[i]+=pointB[i]
pointE[i]+=pointC[i]
# divide by 3
for i in range(0,3):
pointE[i] = pointE[i]/3.0
# start point D with the X and Z coordinates of pointE
pointD = [0,0,0]
pointD[0] = pointE[0]
pointD[2] = pointE[2]
distanceAE = math.sqrt((pointE[0]*pointE[0])+(pointE[2]*pointE[2]))
# set the Y coordinate of point D
pointD[1] = math.sqrt(size*size-distanceAE*distanceAE)
faces=[]
faces.append(cmds.polyCreateFacet(p=[pointA,pointB,pointC],texture=1))
faces.append(cmds.polyCreateFacet(p=[pointA,pointD,pointB],texture=1))
faces.append(cmds.polyCreateFacet(p=[pointB,pointD,pointC],texture=1))
faces.append(cmds.polyCreateFacet(p=[pointC,pointD,pointA],texture=1))
cmds.select(faces[0],replace=True)
for i in range(1,len(faces)):
cmds.select(faces[i],add=True)
# combine all the faces into a single object
obj = cmds.polyUnite()
# merge duplicated vertices
cmds.select(obj[0]+".vtx[:]")
cmds.polyMergeVertex(distance=0.0001)
cmds.select(obj[0])
# move the object to the center
cmds.move(-pointE[0],0,-pointE[2])
# move the pivot of the object
cmds.xform(pivots=(pointE[0],0,pointE[2]))
# freeze transformation
cmds.makeIdentity(apply=True)
# delete construction history
cmds.delete(ch=True)
makeTetra(5)
End –Cheng Gu