
This article focuses on an algorithm for solving problems such as dynamic connectivity, using a data structure called Union Find.
The Evolutionary history of Union Find is From Quick Find –> Union Find –> Weighted Union Find
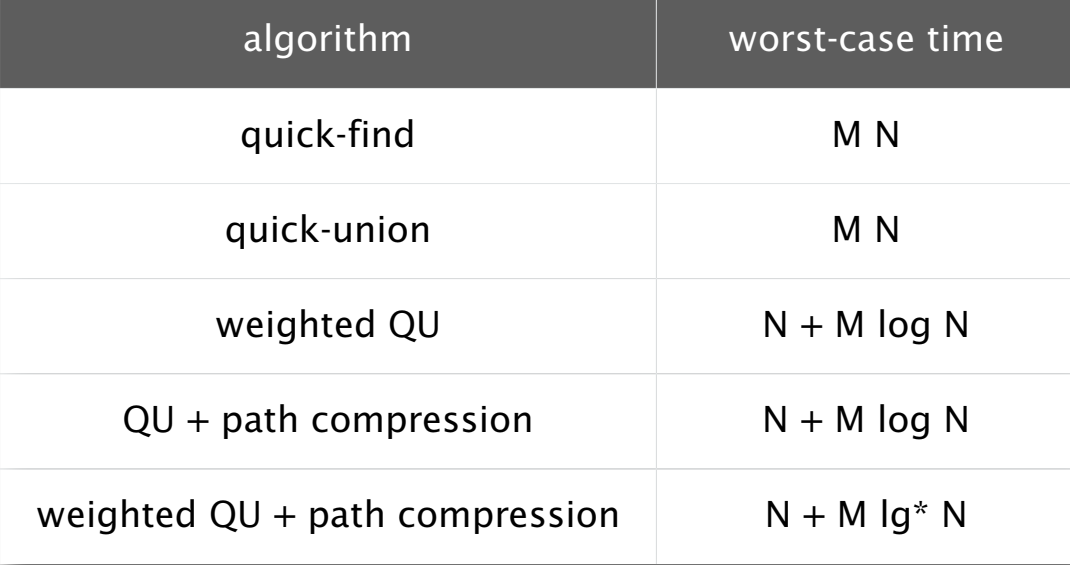
This is the Performance consumption table:
Code:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = StdIn.readInt();
UF uf = new UF(N);
while (!StdIn.isEmpty())
{
int p = StdIn.readInt();
int q = StdIn.readInt();
if (!uf.connected(p, q))
{
uf.union(p, q);
StdOut.println(p + " " + q);
}
}
}

Code:
public class QuickFindUF
{
private int[] id;
private int count;
public QuickFindUF(int N)
{
id = new int[N];
count =N;
// Set ID of earch object to itself
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
id[i] = i;
}
// check if p and q are in the same component
public boolean connected(int p, int q)
{
return id[p] == id[q];
}
// find the id for the given index
public int find(int p)
{
return id[p];
}
public int count()
{
return count;
}
// change all id[p] to id[q]
public void union(int p, int q)
{
int pid = id[p];
int qid = id[q];
for (int i = 0; i < id.length; i++)
if (id[i] == pid) id[i] = qid;
count--;
}
}

Code:
public class QuickUnionUF
{
private int[] id;
private int count;
public QuickUnionUF(int N)
{
id = new int[N];
count =N;
// Set ID of earch object to itself
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
id[i] = i;
}
// check if p and q have same root
public boolean connected(int p, int q)
{
return root(p) == root(q);
}
// find the id for the given index
public int find(int i)
{
return id[i];
}
public int root(int i)
{
//chase parent pointers until reach root
while(i!=id[i])
{
// Make every other node in path point to its grandparent
id[i] = id[id[i]]; // Pass Compression
i = id[i];
}
return i;
}
public int count()
{
return count;
}
// change all id[p] to id[q]
public void union(int p, int q)
{
int pRoot = root(p);
int qRoot = root(q);
if(pRoot == qRoot) return;
id[pRoot] = qRoot; // change root of p to point to root of q
count--;
}
}

Code:
public class WeightedQuickUnionUF
{
private int[] id;
private int[] size; // to count number of objs in the each root
private int count;
public WeightedQuickUnionUF(int N)
{
id = new int[N];
size = new int[N];
count = N;
// Set ID of earch object to itself
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
id[i] = i;
}
// check if p and q have same root
public boolean connected(int p, int q)
{
return root(p) == root(q);
}
// find the id for the given index
public int find(int i)
{
return id[i];
}
public int root(int i)
{
//chase parent pointers until reach root
while(i!=id[i])
{
// Make every other node in path point to its grandparent
id[i] = id[id[i]]; // Pass Compression
i = id[i];
}
return i;
}
public int count()
{
return count;
}
// change all id[p] to id[q]
public void union(int p, int q)
{
int pRoot = root(p);
int qRoot = root(q);
if(pRoot == qRoot) return;
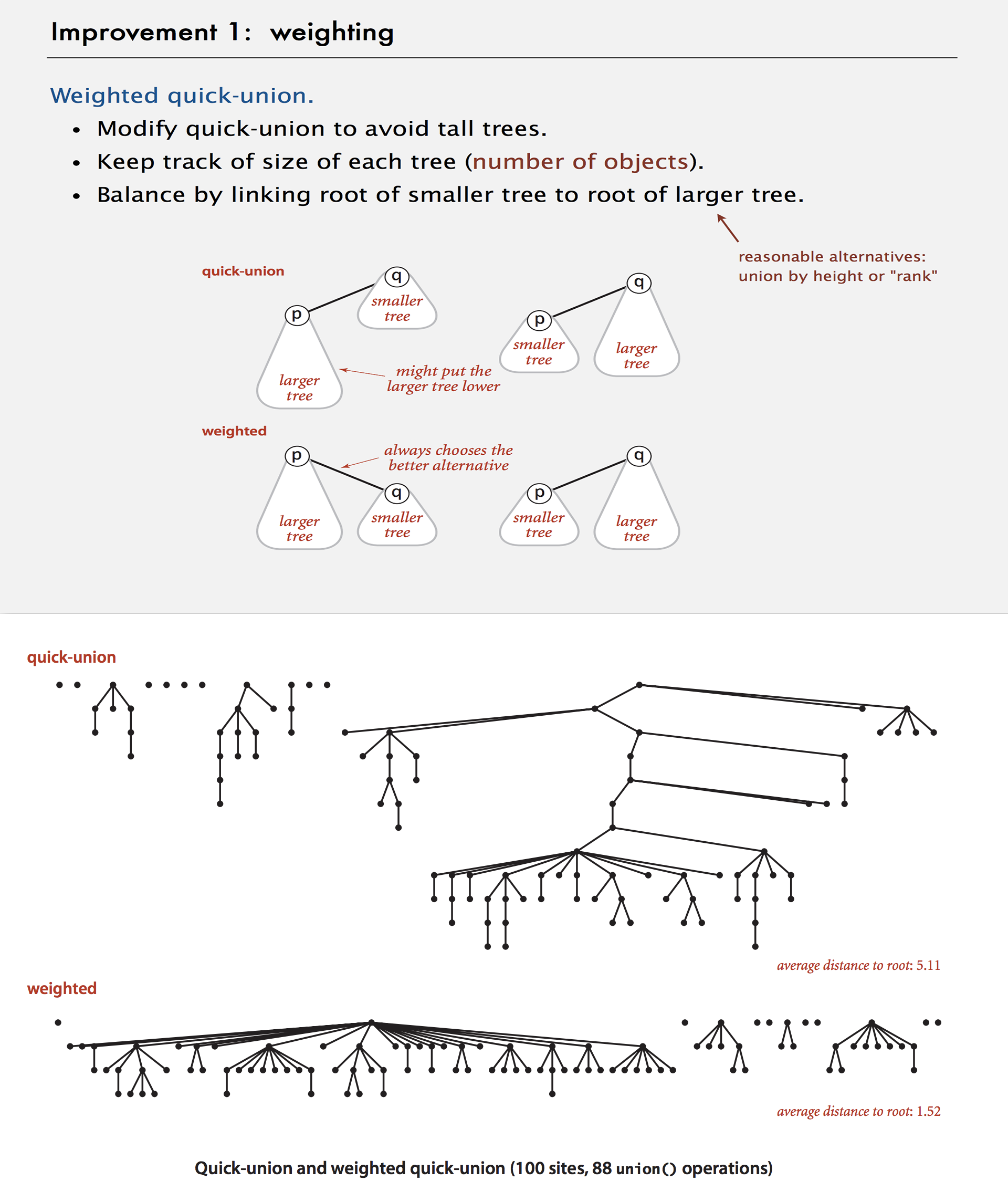
// Link root of smaller tree to root of larger tree
if(size[pRoot] < size[qRoot])
{
id[qRoot] = pRoot;// change root of q to point to root of p
size[pRoot] += size[qRoot]; // update the tree size
}
else
{
id[pRoot] = qRoot;// change root of p to point to root of q
size[qRoot] += size[pRoot]; // update the tree size
}
count--;
}
}
End –Cheng Gu