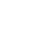

Depth Texture is a RenderTexture that stores the depth value, range is [0,1]. The depth value is calculated from the normalized device coordinates(NDC) obtained after the vertex transformation. The depth value refers to the distance in the z axis and it doesn't represent the distance from the point to the camera. (shown as below image)
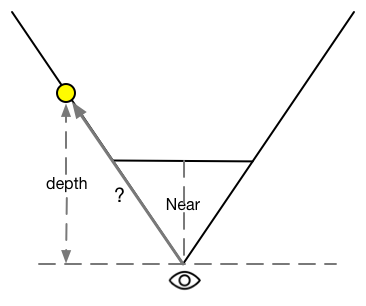
As we all know, in order to render the model on the screen, we have to use this model’s vertix position multiply MVP Matrix to transform the model’s vertices from object space to perspective space. (The process is shown as below image)
first part shows that before the projection transformation, the structure of the frustum and the corresponding vertex position in the view space.second part of the image shows that the transformation result of applying perspective matrix.last part shows that the normailized Device Coordinates.The depth value is just the
remapped value of NPC's z-axis. The reason that needs to remap the depth value is because the range of NPC’s z-axis is [-1,1]. The formula $ 0.5*Z_ndc+0.5 $ can map it from [-1,1] to [0,1].
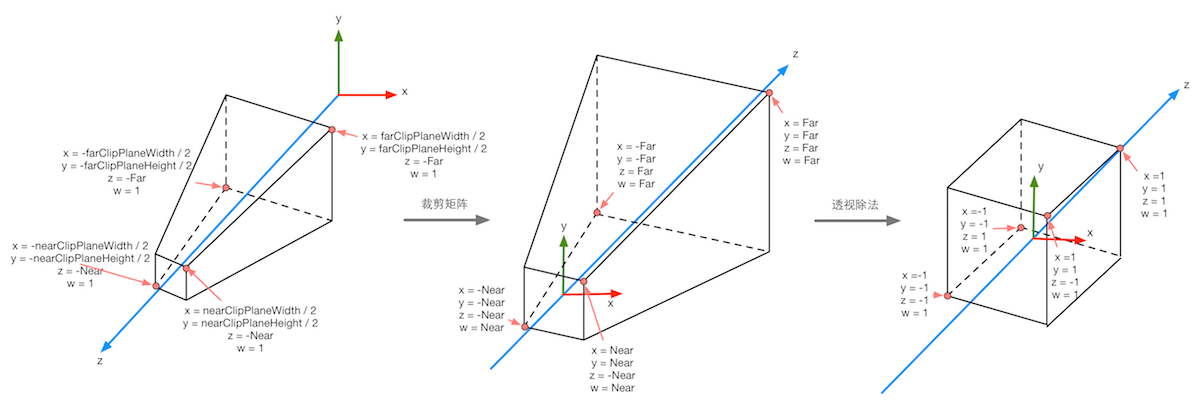
Similar to the depth texture, this will be a screen-size texture. However, instead of storing the depth of each pixel, it’ll store its normal info in view space.
Below Image shows the differences between depth and normal texture:
In Unity, there are two major rendering path which are forward rendering and deferred rendering. When we are using deferred rendering path, we can get the depth texture directly, because deferred rendering will store these info into the G-Buffer. However, when we are using forward rendering path, we have to use an additional Pass to get, which is the Pass (LightMode = "ShadowCaster") that casts the shadow.
Note: Unity uses the shader replacement technique to render objects with a RenderType of Opauqe and a queue of less than 2500 (Background, Geometry, Alphatest, opaque queues) into deep textures and normal textures.
Method of access and use:
depthTextureMode of Camera: camera.depthTextureMode = DepthTextureMode.Depth;_CameraDepthTexture access in Shdaer: float d = SAMPLE_DEPTH_TEXTURE(_CameraDepthTexture, i.uv);Code example to get Linear depth value:
float depth = SAMPLE_DEPTH_TEXTURE(_CameraDepthTexture, i.uv);
float linearDepth = Linear01Depth(depth);
return fixed4(linearDepth, linearDepth, linearDepth, 1.0);
Another option is to create both Depth Texture and Normal Texture. In deferred rendering path, normral info is easy to get acess as well. But in forward rendering path, unity uses a Pass to render the whole scene one more time to get the normal info.(Source Code is in the Internal-DepthNormalsTexture.shader)
Method of access and use:
depthTextureMode of Camera: camera.depthTexureMode = DepthTextureMode.DepthNormals;_CameraDepthNormalsTexture access in shader: float3 nt = tex2D(_CameraDepthNormalsTexture, i.uv);DecodeDepthNormal which can get the depth in zw component and normal in xy component. inline void DecodeDepthNormal(float4 enc, out float depth, out float3 normal)
{
depth = DecodeFloatRG(enc.zw);
normal = DecodeViewNormalStereo(enc);
}
Code example to get normal direction:
fixed3 normal = DecodeViewNormalStereo(tex2D(_CameraDepthNormalsTexture, i.uv).xy);
return fixed4(normal * 0.5 + 0.5, 1);
Relative Functions:
LinearEyeDepth:The depth sampling results are converted to the perspective space. z value in view spaceLinear01Depth:Returns the linear depth value in the range [0, 1].DecodeDepthNormal:decoded to get depth and normal information from the sampling results.DecodeFloatRG:decode to get depth info.DecodeViewNormalStereo:decode to get normal info.
End –Cheng Gu