
In CG, CubeMap is the way to achieve Environment Mapping. it can simulate the environment around the object, make the object be able to reflect the environment around itself.
Cubemap includes 6 images. these images correspond to the six sides of a cube.
So How to sample this Cubemap Texture?
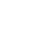
Different from sampling the 2D Texture, it needs a 3D Texture coordinate to sample a Cubemap. This 3D texture coordiate represents a 3D direction vector of a object in the world space. This Vector starts from the center of the cube, And a direction vector only represent the dir, so it can be think of infinity length, when it extend its length, eventually it will intersect with one of the cube’s six textures, the result of sampling is calculated with the intersection point. just like below image.
Pros of using Cubemap
Cons of using Cubemap
- When introducing a new object in the scene, the light source, or an object moves, we need to regenerate the cube texture.
- The Cubemap texture can not simulate the result of the multiple reflections, such as two metal ball reflection of each other.
Therefore, we should use Cubemap texture for convex objects and do not use it for concave objects (because the concave objects reflect itself)
To simulate the reflection effect, we simply need to calculate the direction of the reflection by the direction of the incident ray(which is the negative view direction) and the normal direction of the surface. Finally, the reflection direction is used to sample the Cubemap texture.

Properties:
Properties
{
_Color("Color",Color) = (1,1,1,1)
_ReflectColor("Reflect Color", Color) = (1,1,1,1)
_ReflectAmount("Reflect Amount", Range(0,1)) = 1
_Cubemap("Reflection Cubemap", Cube) = "_Skybox"{}
}
VertexShader:
v2f vert(a2v v)
{
v2f f;
f.pos = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
f.worldPos = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, v.vertex).xyz;
f.worldNormal = mul(v.normal,unity_WorldToObject);
f.worldViewDir = UnityWorldSpaceViewDir(f.worldPos);
f.worldRefl = reflect(-f.worldViewDir,f.worldNormal);
TRANSFER_SHADOW(f);
return f;
}
FragmentShader:
fixed4 frag(v2f f):SV_Target
{
fixed3 worldNormal = normalize(f.worldNormal);
fixed3 worldLightDir = normalize(UnityWorldSpaceLightDir(f.worldPos));
fixed3 ambient = UNITY_LIGHTMODEL_AMBIENT.rgb;
fixed3 diffuse = _LightColor0.rgb * _Color.rgb *max(0, dot(worldNormal,worldLightDir));
fixed3 reflection = texCUBE(_Cubemap,f.worldRefl).rgb * _ReflectColor.rgb;
UNITY_LIGHT_ATTENUATION(atten, f, f.worldPos);
fixed3 color = ambient+lerp(diffuse,reflection,_ReflectAmount)*atten;
return fixed4(color,1.0);
}
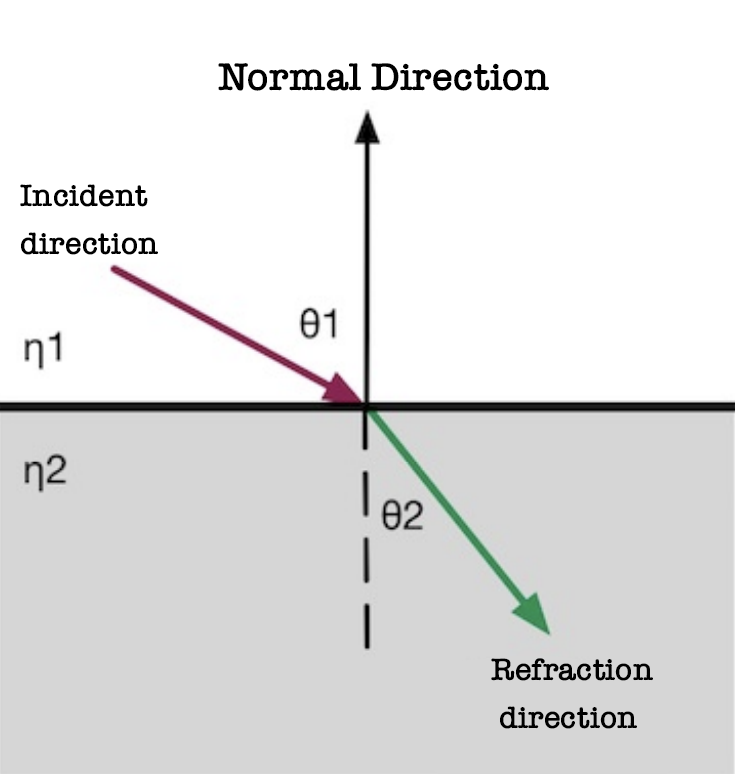
Refraction: When light rays from one medium, such as air, are deflected into another, such as glass, the direction of propagation generally changes, this phenomenon is called refraction.
Snell’s Law:

n1 and n2 are the medium’s percentage of refraction.
Result:

Properties:
_Color("Color",Color) = (1,1,1,1)
_RefractColor("Reflect Color", Color) = (1,1,1,1)
_RefractAmount("Reflect Amount", Range(0,1)) = 1
// The Percentage of Differnet Medium
// eg: Refraction Percentage of Air/ Refraction Percentage of Glass
_RefractRatio("Refract Ratio",Range(0.1,1)) = 0.5
_Cubemap("Reflection Cubemap", Cube) = "_Skybox"{}
VertexShader:
v2f vert(a2v v)
{
v2f f;
f.pos = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
f.worldPos = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, v.vertex).xyz;
f.worldNormal = mul(v.normal,unity_WorldToObject);
f.worldViewDir = UnityWorldSpaceViewDir(f.worldPos);
f.worldRefr = refract(-normalize(f.worldViewDir),normalize(f.worldNormal),_RefractRatio);
TRANSFER_SHADOW(f);
return f;
}
FragmentShader:
fixed4 frag(v2f f):SV_Target
{
fixed3 worldNormal = normalize(f.worldNormal);
fixed3 worldLightDir = normalize(UnityWorldSpaceLightDir(f.worldPos));
fixed3 ambient = UNITY_LIGHTMODEL_AMBIENT.rgb;
fixed3 diffuse = _LightColor0.rgb * _Color.rgb *max(0, dot(worldNormal,worldLightDir));
fixed3 refraction = texCUBE(_Cubemap,f.worldRefr).rgb * _RefractColor.rgb;
UNITY_LIGHT_ATTENUATION(atten, f, f.worldPos);
fixed3 color = ambient+lerp(diffuse,refraction,_RefractAmount)*atten;
return fixed4(color,1.0);
}
Fresnel Reflection Represents a Optical Phenomenon. When light hits the surface of an object, some parts occur reflection, some parts goes into the inside of the object, or occur refraction or scattering.
For example, When you stand by the lake and look down at the water at your feet, you will find that the water is almost transparent. You can see the small fish and stones directly. But when you look up at the water in the distance, you will find that you can hardly see the underwater scene, but only the environment that reflects the water.
A Famous Equation is called Schlick’s Approximation

In this equation, F0 is a reflection coefficient, which is used to control the magnitude of the reflection, v is the view dir, n is normal dir.

Properties:
_Color("Color",Color) = (1,1,1,1)
_FresnelScale("Fresnel Scale",Range(0,1))=0.5
_Cubemap("Reflection Cubemap", Cube) = "_Skybox"{}
VertexShader:
v2f vert(a2v v)
{
v2f f;
f.pos = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
f.worldPos = mul(unity_ObjectToWorld, v.vertex).xyz;
f.worldNormal = mul(v.normal,unity_WorldToObject);
f.worldViewDir = UnityWorldSpaceViewDir(f.worldPos);
f.worldRefl = reflect(-f.worldViewDir,f.worldNormal);
TRANSFER_SHADOW(f);
return f;
}
FragmentShader:
fixed4 frag(v2f f):SV_Target
{
fixed3 worldNormal = normalize(f.worldNormal);
fixed3 worldLightDir = normalize(UnityWorldSpaceLightDir(f.worldPos));
fixed3 worldViewDir = normalize(f.worldViewDir);
fixed3 ambient = UNITY_LIGHTMODEL_AMBIENT.rgb;
fixed3 diffuse = _LightColor0.rgb * _Color.rgb *max(0, dot(worldNormal,worldLightDir));
fixed3 reflection = texCUBE(_Cubemap,f.worldRefl).rgb;
fixed fesnel = _FresnelScale+(1-_FresnelScale)*pow(1-dot(worldViewDir,worldNormal),5);
UNITY_LIGHT_ATTENUATION(atten, f, f.worldPos);
fixed3 color = ambient+lerp(diffuse, reflection, fesnel) * atten;
return fixed4(color,1.0);
}
End –Cheng Gu