
Bump mapping is used for giving models more details with cheap costs by modifying the normal of the model .
This method doesn’t change the models detail level, but give us a visual effect that the model has more details after bump mapping.
There are two common ways to do the bump mapping, which are Height Mapping, and Normal Mapping.

Use a height map to simulate the surface displacement. If the color are darker, the surface are lower; if the color are lighter, the surface are higher. The advantage of this using height map is make the height of the surface more obviouse to see. But it is also more expensive performance.
Normally we will use normal map to modify the light. In Normal map, it represents the direction of the normal. The range of normal’s component range is [-1,1], but the pixel’s component range is [0,1].So that we need to do a mapping
Pixel = (Normal + 1) / 2
This will require us to use a inverse function to get the original normal direction after mapping the pixel in the Shader
Normal = Pixel x 2 - 1
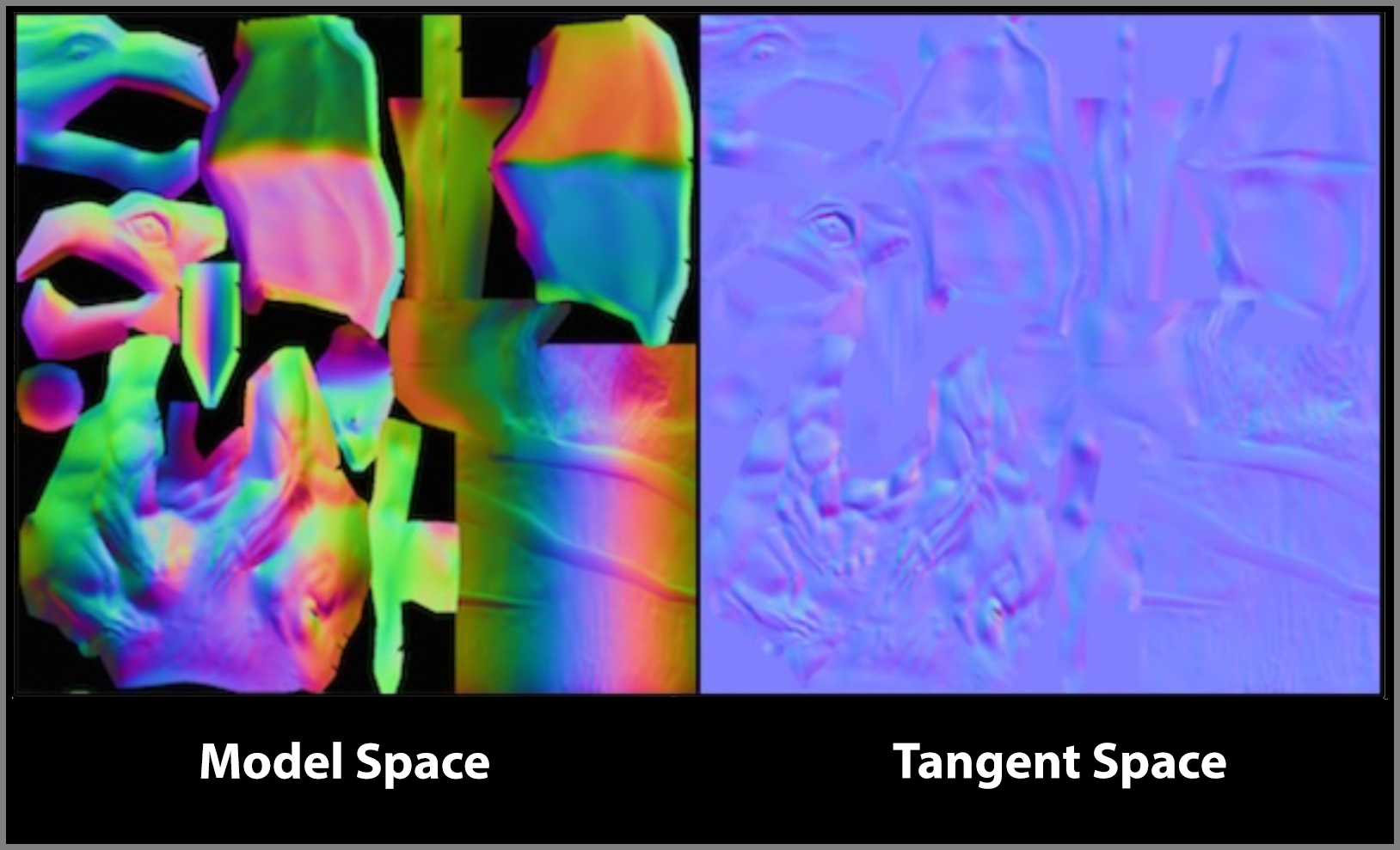
The above image respectively gives us the normal map in the model space and tangent space.
The advantage in the tangent space to calculate normal mapping is more efficient don’t need too many conversion.
Shader "MyShader/NormalMapInTangentSpace"
{
Properties
{
_Color("Color",Color) = (1,1,1,1)
_MainTex ("Texture", 2D) = "white" {}
_BumpMap("Normal Map",2D) = "bump" {}
_BumpScale("Bump Scale",Float) = 1.0
_Specular("Specular",Color) = (1,1,1,1)
_Gloss("Gloss",Range(5,100)) = 5
}
SubShader
{
Pass
{
Tags{"LightMode" = "ForwardBase"}
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "Lighting.cginc"
fixed4 _Color;
sampler2D _MainTex;
float4 _MainTex_ST;
sampler2D _BumpMap;
float4 _BumpMap_ST;
float _BumpScale;
fixed4 _Specular;
float _Gloss;
struct a2v
{
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float3 normal : NORMAL;
// We use TANGENT semantic to describe a float4 type variable tangent,
// to tell CG give the vertices' tangent direction to the variable tangent.
// compared with normal, tangent is a float4 variable,
// because we need tangent.w to determine the binormal's direction
float4 tangent : TANGENT;
float4 texcoord : TEXCOORD0;
};
struct v2f
{
float4 pos : SV_POSITION;
float4 uv : TEXCOORD0;
float3 lightDir : TEXCOORD1;
float3 viewDir : TEXCOORD2;
};
v2f vert(a2v v)
{
v2f o;
o.pos = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
o.uv.xy = v.texcoord.xy * _MainTex_ST.xy + _MainTex_ST.zw;
o.uv.zw = v.texcoord.xy * _BumpMap_ST.xy + _BumpMap_ST.zw;
// Compute the binormal
// float3 binormal = cross( normalize(v.normal), normalize(v.tangent.xyz) ) * v.tangent.w;
// Construct a matrix which transform vectors from object space to tangent space
// float3x3 rotation = float3x3(v.tangent.xyz, binormal, v.normal);
// Or just use the built-in macro
TANGENT_SPACE_ROTATION;
// Transform the light direction from object space to tangent space
o.lightDir = mul(rotation, normalize(ObjSpaceLightDir(v.vertex))).xyz;
// Transform the view direction from object space to tangent space
o.viewDir = mul(rotation, normalize(ObjSpaceViewDir(v.vertex))).xyz;
return o;
}
fixed4 frag(v2f f) : SV_Target
{
fixed3 tangentLightDir = normalize(f.lightDir);
fixed3 tangentViewDir = normalize(f.viewDir);
fixed4 packedNormal = tex2D(_BumpMap,f.uv.zw);
// if the texture is not marked as "Normal Map"
//fixed3 tangentNormal;
//tangentNormal.xy =(packedNormal.xy * 2 - 1) * _BumpScale;
//else
fixed3 tangentNormal = UnpackNormal(packedNormal);
tangentNormal.xy *= _BumpScale;
tangentNormal.z = sqrt(1.0 - saturate(dot(tangentNormal.xy, tangentNormal.xy)));
fixed3 albedo = tex2D(_MainTex, f.uv.xy).rgb * _Color.rgb;
fixed3 ambient = UNITY_LIGHTMODEL_AMBIENT.xyz * albedo;
fixed3 diffuse = _LightColor0.rgb * albedo * saturate(dot(tangentNormal,tangentLightDir));
fixed3 halfDir = normalize(tangentLightDir + tangentViewDir);
fixed3 specular = _LightColor0.rgb * _Specular.rgb * pow(saturate(dot(halfDir, tangentNormal)),_Gloss);
fixed3 c = ambient + diffuse + specular;
return fixed4(c,1);
}
ENDCG
}
}
FallBack "Specular"
}
However, from a general point of view, normal mapping in world space is better than in tangent space. For example if we need to use Cubemap to mapping the environment we have to
Shader "MyShader/NormalMapInWorldSpace"
{
Properties
{
_Color ("Color Tint", Color) = (1, 1, 1, 1)
_MainTex ("Main Tex", 2D) = "white" {}
_BumpMap ("Normal Map", 2D) = "bump" {}
_BumpScale ("Bump Scale", Float) = 1.0
_Specular ("Specular", Color) = (1, 1, 1, 1)
_Gloss ("Gloss", Range(8.0, 256)) = 20
}
SubShader
{
Pass
{
Tags { "LightMode"="ForwardBase" }
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "Lighting.cginc"
fixed4 _Color;
sampler2D _MainTex;
float4 _MainTex_ST;
sampler2D _BumpMap;
float4 _BumpMap_ST;
float _BumpScale;
fixed4 _Specular;
float _Gloss;
struct a2v
{
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float3 normal : NORMAL;
float4 tangent : TANGENT;
float4 texcoord : TEXCOORD0;
};
struct v2f
{
float4 pos : SV_POSITION;
float4 uv : TEXCOORD0;
float4 TtoW0 : TEXCOORD1;
float4 TtoW1 : TEXCOORD2;
float4 TtoW2 : TEXCOORD3;
};
v2f vert(a2v v)
{
v2f o;
o.pos = mul(UNITY_MATRIX_MVP, v.vertex);
o.uv.xy = v.texcoord.xy * _MainTex_ST.xy + _MainTex_ST.zw;
o.uv.zw = v.texcoord.xy * _BumpMap_ST.xy + _BumpMap_ST.zw;
float3 worldPos = mul(_Object2World, v.vertex).xyz;
fixed3 worldNormal = UnityObjectToWorldNormal(v.normal);
fixed3 worldTangent = UnityObjectToWorldDir(v.tangent.xyz);
fixed3 worldBinormal = cross(worldNormal, worldTangent) * v.tangent.w;
// Compute the matrix that transform directions from tangent space to world space
// Put the world position in w component for optimization
o.TtoW0 = float4(worldTangent.x, worldBinormal.x, worldNormal.x, worldPos.x);
o.TtoW1 = float4(worldTangent.y, worldBinormal.y, worldNormal.y, worldPos.y);
o.TtoW2 = float4(worldTangent.z, worldBinormal.z, worldNormal.z, worldPos.z);
return o;
}
fixed4 frag(v2f i) : SV_Target
{
// Get the position in world space
float3 worldPos = float3(i.TtoW0.w, i.TtoW1.w, i.TtoW2.w);
// Compute the light and view dir in world space
fixed3 lightDir = normalize(UnityWorldSpaceLightDir(worldPos));
fixed3 viewDir = normalize(UnityWorldSpaceViewDir(worldPos));
// Get the normal in tangent space
fixed3 bump = UnpackNormal(tex2D(_BumpMap, i.uv.zw));
bump.xy *= _BumpScale;
bump.z = sqrt(1.0 - saturate(dot(bump.xy, bump.xy)));
// Transform the narmal from tangent space to world space
bump = normalize(half3(dot(i.TtoW0.xyz, bump), dot(i.TtoW1.xyz, bump), dot(i.TtoW2.xyz, bump)));
fixed3 albedo = tex2D(_MainTex, i.uv).rgb * _Color.rgb;
fixed3 ambient = UNITY_LIGHTMODEL_AMBIENT.xyz * albedo;
fixed3 diffuse = _LightColor0.rgb * albedo * max(0, dot(bump, lightDir));
fixed3 halfDir = normalize(lightDir + viewDir);
fixed3 specular = _LightColor0.rgb * _Specular.rgb * pow(max(0, dot(bump, halfDir)), _Gloss);
return fixed4(ambient + diffuse + specular, 1.0);
}
ENDCG
}
}
FallBack "Specular"
}
End –Cheng Gu